In previous story we learnt how to create restful crud(create, read, update, delete) api in nodejs, express and mongodb but now in this we’ll learn to create crud api in
nodejs , express and mysql .
Prerequisites and required applications
Node.js is an open source, cross-platform runtime environment for developing server-side and networking applications. You should have basic understanding of nodejs.
ExpressJS is one of the most trending web frameworks for node.js. It is built on top of node.js http module, and adds support for routing, middleware, view system etc. It is very simple and minimal, unlike other frameworks.
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system. Its name is a combination of “My”, the name of co-founder Michael Widenius’s daughter, and “SQL”, the abbreviation for Structured Query Language.
EcmaScript (ES) is a standardised scripting language for JavaScript (JS). The current ES version supported in modern browsers is ES5. However, ES6 tackles a lot of the limitations of the core language, making it easier for devs to code
Postman is an API(application programming interface) development tool which helps to build, test and modify APIs.It has the ability to make various types of HTTP requests(GET, POST, PUT, PATCH etc.).
IDE (integrated development environment) is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to computer programmers for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source code editor, build automation tools, and a debugger. In case of mine, I prefer to use visual studio code.
Create a Project
Now it’s time to create our project. Create a directory name
NodeMysqlCrudApp. Then navigate to NodeMysqlCrudApp directory. Command are as below// Create directory mkdir NodeMysqlCrudApp// then Navigate to NodeMysqlCrudApp cd NodeMysqlCrudApp
Initialise and Configure Our Project
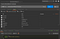
To initialise run the command in project folder
npm init that will ask a few questions to avoid that you can run npm init -y . Finally package.json looks like below
Install express and other dependencies
- Express is top framework of nodejs. Install using below command :
npm install express --save
- Body Parser is Node.js body parsing middleware. Parse incoming request bodies in a middleware before your handlers, available under the
req.bodyproperty.
npm install body-parser --save
- MySQL is open source database use to interacting with database and manipulating the records.
npm install mysql --save
- Nodemon is a tool that helps develop node.js based applications by automatically restarting the node application when file changes in the directory are detected. Use
-devflag to save in devDependencies and--savewill save the dependencies in package.json file.
npm install --save-dev nodemon
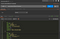
Now
package.json looks like as below
Start the web server
As we earlier we have created enter point of application is
server.js, we will create server.js file at the root of project folder.touch server.js
Add some code in
server.js fileconst express = require('express'); const bodyParser = require('body-parser');// create express app const app = express();// Setup server port const port = process.env.PORT || 5000;// parse requests of content-type - application/x-www-form-urlencoded app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }))// parse requests of content-type - application/json app.use(bodyParser.json())// define a root route app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send("Hello World"); });// listen for requests app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Server is listening on port ${port}`); });
Now run the web server using
node server.js or node server command :node server.jsORnode server
Now open your favourite browser and navigate to
http://localhost:5000 . Browser will show Hello World . That’s great now our server is running.
In previous step we had installed
nodemon . If we want run the server using nodemon then we have to use the nodemon server.js or nodemon server command. Let’s do some change in package.json file , add a line of code in scripts object of package.json file."start": "nodemon server"

Now simply run
npm start to run the server that will auto restart the serve when detect any change in files.npm start
Create database
CREATE DATABASE node_mysql_crud_db;CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `employees` ( `id` BIGINT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT, `first_name` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, `last_name` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, `email` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, `phone` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, `organization` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, `designation` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, `salary` DECIMAL(11,2) UNSIGNED DEFAULT 0.00, `status` TINYINT UNSIGNED DEFAULT 0, `is_deleted` TINYINT UNSIGNED DEFAULT 0, `created_at` DATETIME NOT NULL, `updated_at` DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE = InnoDB;INSERT INTO `node_mysql_crud_db`.`employees` (`first_name`, `last_name`, `email`, `phone`, `organization`, `designation`, `salary`, `status`, `is_deleted`, `created_at`) VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'johndoe@gmail.com', '1234567890', 'BR Softech Pvt Ltd', 'Full Stack Developer', '500.00', '1', '0', '2019-11-19 03:30:30'); INSERT INTO `node_mysql_crud_db`.`employees` (`first_name`, `last_name`, `email`, `phone`, `organization`, `designation`, `salary`, `status`, `is_deleted`, `created_at`) VALUES ('Jane', 'Doe', 'janedoe@gmail.com', '9876543210', 'RG Infotech Jaipur', 'PHP Developer', '450.00', '1', '0', '2019-11-19 03:35:30');
Make database connection
To make connectivity with database in our project we’ll make seperate file. So create a
config folder at root and make a db.config.js file inside config folder.mkdir config
cd config
touch db.config.js
Now open
db.config.js and add code below for creating mysql connection.'use strict';const mysql = require('mysql');//local mysql db connectionconst dbConn = mysql.createConnection({ host : 'localhost', user : 'root', password : '', database : 'node_mysql_crud_db'});dbConn.connect(function(err) { if (err) throw err; console.log("Database Connected!");});module.exports = dbConn;
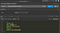
Project Folder Structure
Now folder structure of project like as below

Complete
employee.model.js file is here -'use strict';var dbConn = require('./../../config/db.config');//Employee object createvar Employee = function(employee){ this.first_name = employee.first_name; this.last_name = employee.last_name; this.email = employee.email; this.phone = employee.phone; this.organization = employee.organization; this.designation = employee.designation; this.salary = employee.salary; this.status = employee.status ? employee.status : 1; this.created_at = new Date(); this.updated_at = new Date();};Employee.create = function (newEmp, result) {dbConn.query("INSERT INTO employees set ?", newEmp, function (err, res) {if(err) { console.log("error: ", err); result(err, null);}else{ console.log(res.insertId); result(null, res.insertId);}});};Employee.findById = function (id, result) {dbConn.query("Select * from employees where id = ? ", id, function (err, res) {if(err) { console.log("error: ", err); result(err, null);}else{ result(null, res);}});};Employee.findAll = function (result) {dbConn.query("Select * from employees", function (err, res) {if(err) { console.log("error: ", err); result(null, err);}else{ console.log('employees : ', res); result(null, res);}});};Employee.update = function(id, employee, result){dbConn.query("UPDATE employees SET first_name=?,last_name=?,email=?,phone=?,organization=?,designation=?,salary=? WHERE id = ?", [employee.first_name,employee.last_name,employee.email,employee.phone,employee.organization,employee.designation,employee.salary, id], function (err, res) {if(err) { console.log("error: ", err); result(null, err);}else{ result(null, res);}});};Employee.delete = function(id, result){dbConn.query("DELETE FROM employees WHERE id = ?", [id], function (err, res) {if(err) { console.log("error: ", err); result(null, err);}else{ result(null, res);}});};module.exports= Employee;
Here is complete
employee.controller.js file -'use strict';const Employee = require('../models/employee.model');exports.findAll = function(req, res) {Employee.findAll(function(err, employee) { console.log('controller') if (err) res.send(err); console.log('res', employee); res.send(employee);});};exports.create = function(req, res) {const new_employee = new Employee(req.body);//handles null errorif(req.body.constructor === Object && Object.keys(req.body).length === 0){ res.status(400).send({ error:true, message: 'Please provide all required field' });}else{Employee.create(new_employee, function(err, employee) { if (err) res.send(err); res.json({error:false,message:"Employee added successfully!",data:employee});});}};exports.findById = function(req, res) {Employee.findById(req.params.id, function(err, employee) { if (err) res.send(err); res.json(employee);});};exports.update = function(req, res) { if(req.body.constructor === Object && Object.keys(req.body).length === 0){ res.status(400).send({ error:true, message: 'Please provide all required field' }); }else{ Employee.update(req.params.id, new Employee(req.body), function(err, employee) { if (err) res.send(err); res.json({ error:false, message: 'Employee successfully updated' });});}};exports.delete = function(req, res) {Employee.delete( req.params.id, function(err, employee) { if (err) res.send(err); res.json({ error:false, message: 'Employee successfully deleted' });});};
Here is complete
employee.routes.js file -const express = require('express')const router = express.Router()const employeeController = require('../controllers/employee.controller');// Retrieve all employeesrouter.get('/', employeeController.findAll);// Create a new employeerouter.post('/', employeeController.create);// Retrieve a single employee with idrouter.get('/:id', employeeController.findById);// Update a employee with idrouter.put('/:id', employeeController.update);// Delete a employee with idrouter.delete('/:id', employeeController.delete);module.exports = router
Now finally complete
server.js file here :const express = require('express');const bodyParser = require('body-parser');// create express appconst app = express();// Setup server portconst port = process.env.PORT || 5000;// parse requests of content-type - application/x-www-form-urlencodedapp.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }))// parse requests of content-type - application/jsonapp.use(bodyParser.json())// define a root routeapp.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send("Hello World");});// Require employee routesconst employeeRoutes = require('./src/routes/employee.routes')// using as middlewareapp.use('/api/v1/employees', employeeRoutes)// listen for requestsapp.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Server is listening on port ${port}`);});
API End Points
- GET /api/v1/employees: will give all employees stored in database
- GET /api/v1/employees/<employee_id>: will give a specific employee with employee_id.
- POST /api/v1/employees : create a employee
- PATCH /api/v1/employees/<employee_id>: update a employee partially
- DELETE /api/v1/employees/<employee_id>: delete a employee
- PUT /api/v1/employees/<employee_id>: update a employee completely
APIs Test in Postman
Creating a new employee
api/v1/employees using POST method
Get all employees list
api/v1/employees using GET method
Get specific employee
api/v1/employees/id using GET method
Update specific employee
api/v1/employees/id using PUT method
Delete specific employee
api/v1/employees/id using DELETE method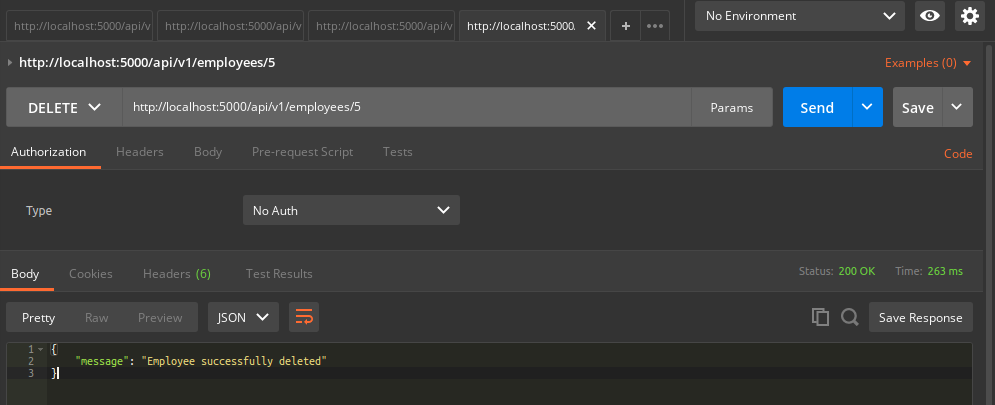
You can find it on git repository here.
https://github.com/rahulguptafullstack/node-mysql-crud-app
Thank for reading.

Comments
Post a Comment